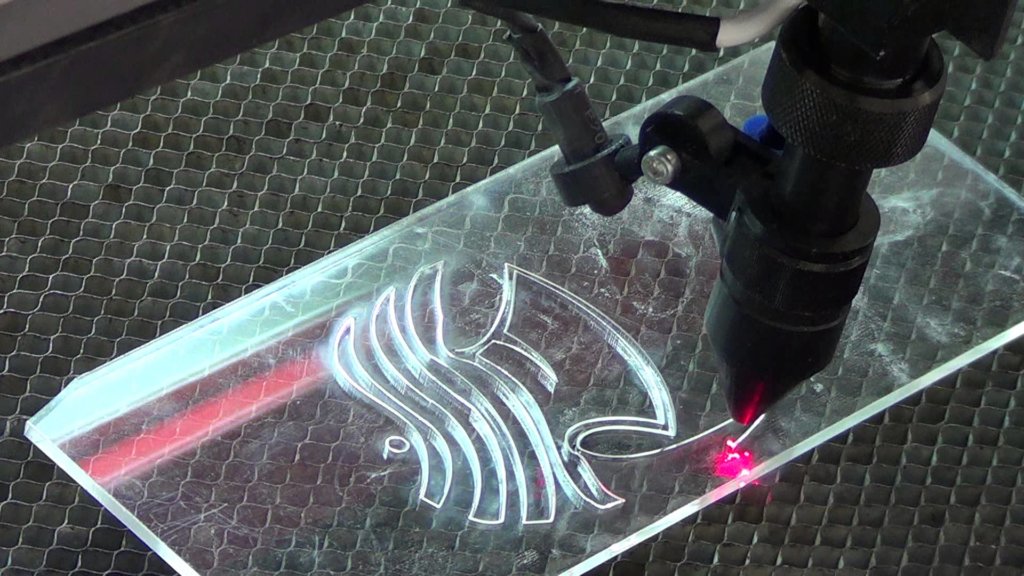
What Materials Can The Laser Engraving Machine Engrave
LaserPecker 3 laser engraving machine is a high-precision, high-efficiency processing equipment, widely used in various industries and fields. So, what materials can a laser engraving machine engrave? This article will focus on this issue in detail.
The Working Principle Of Laser Engraving Machine
Before understanding what materials a laser engraving machine can engrave, we need to understand how a laser engraving machine works. To put it simply, when the laser engraving machine works, it irradiates the surface of the material with a laser beam, and uses techniques such as ablation, vaporization, and oxidation to cut off a layer of the surface of the material, thereby realizing the engraving of patterns, characters, etc.
In the Laserpecker 2 laser engraving machine, the core part is the laser, the laser beam generated by it can be focused into a very small diameter after the optical path is designed to increase the power density of the laser beam. At the same time, in order to ensure that the laser beam can accurately scan to the position to be engraved, the laser engraving machine also needs to be equipped with a high-precision displacement control system.
Types Of Materials That Can Be Engraved
1. Non-metallic materials
At present, most laser engraving machines use CO2 lasers. The wavelength of this laser is mainly concentrated at 10.6 microns, and it has strong adaptability to most non-metallic materials. Below are some common non-metallic materials that laser engraving machines can easily engrave:
(1) Wood: including all kinds of wood and wood products, such as plywood, medium density fiberboard, etc.
(2) Paper: all kinds of cardboard, thermal paper, etc.
(3) Leather: genuine leather and artificial leather, etc.
(4) Cloth: all kinds of interwoven fabrics and non-woven fabrics, etc.
(5) Plastic: acrylic, PVC, ABS, etc.
(6) Stone: marble, granite, etc.
2. Metal material
Although Laserpecker laser engraving machines are mainly used in the field of non-metallic materials, the Nd:YAG lasers used in early laser engraving machines can be used for engraving or cutting metal materials such as titanium, aluminum, copper, and stainless steel. However, due to the high price and high maintenance cost of this laser, it was later replaced by CO2 laser.
Applicability Of Laser Engraving Machine
Although the laser engraving machine can engrave a wide range of materials, users also need to consider its applicability when choosing a laser engraving machine. In the laser engraving machine, especially the following aspects need to be paid attention to:
1. Engraving accuracy: Engraving accuracy usually refers to the color error that the laser engraving machine can achieve for many hours within a certain thickness. The smaller the value, the higher the processing accuracy of the laser engraving machine.
2. Engraving area: The engraving area refers to the maximum area that the Atomstack S20 Pro laser engraving machine can engrave. Users need to choose the appropriate area size according to their needs.
3. Engraving speed: The engraving speed refers to the material area that the laser engraving machine can engrave per unit time. The faster the speed, the higher the processing efficiency will be.
4. Material hardness: The laser engraving machine needs to focus the laser beam on the surface of the material through reflection, refraction, etc. Therefore, if the material is too hard or too thick, it may affect the working effect of the laser engraving machine.
5. Material loss: The laser engraving machine will produce a lot of waste and dust during the engraving process, which needs to be cleaned in time, otherwise it may affect the normal operation of the equipment.
To sum up, the laser engraver can engrave a wide range of materials, including wood, paper, leather, cloth, plastic, stone and other non-metallic materials. When choosing a laser engraving machine, users need to choose the appropriate equipment according to their needs and material characteristics to achieve the best processing effect.